Differences between Bare Metal and Cloud Servers, which should I choose?
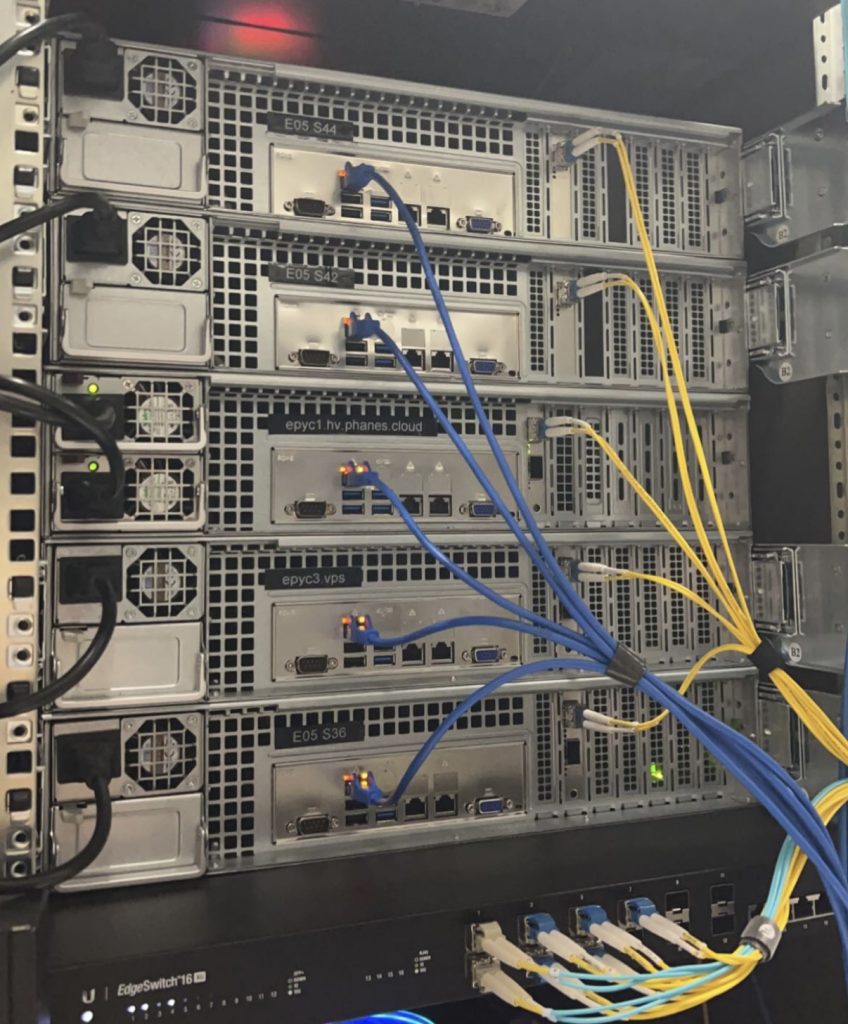

When it comes to hosting your applications or websites, you have two primary options: bare metal servers and cloud servers. Each approach offers unique advantages and drawbacks, and understanding the differences between them is crucial for making an informed decision. In this blog post, we will compare bare metal servers and cloud servers, highlighting their benefits and downsides, to help you choose the most suitable hosting solution for your needs.
Bare Metal Servers
View PricingBenefits of Bare Metal Servers:
- Performance: Bare metal servers provide dedicated hardware resources, offering superior performance compared to virtualized cloud environments. The absence of resource sharing ensures consistent performance even during peak loads, making bare metal servers ideal for resource-intensive applications.
- Customization: With bare metal servers, you have complete control over the hardware and software configurations. This level of customization allows you to optimize the server environment to meet specific requirements, making it a preferred choice for complex or specialized applications.
- Security: Bare metal servers offer enhanced security since they are isolated physical machines. There are no neighboring virtual environments that could potentially pose security risks. This isolation makes bare metal servers suitable for applications that require strict data privacy and compliance.
Downsides of Bare Metal Servers:
- Scalability: Scaling a bare metal infrastructure can be time-consuming and involves manual provisioning and configuration of new hardware. This lack of elasticity makes it less suitable for applications with fluctuating resource demands or rapid scalability requirements.
- Cost: Bare metal servers often come with higher upfront costs compared to cloud servers. Additionally, you are responsible for managing and maintaining the hardware, which can result in additional expenses related to infrastructure management.
Cloud Servers
View PricingBenefits of Cloud Servers:
- Scalability: Cloud servers offer exceptional scalability, allowing you to easily adjust resources based on your requirements. With the ability to add or remove virtual machines on-demand, you can quickly scale your infrastructure to handle traffic spikes or accommodate growing user bases.
- Flexibility: Cloud servers provide flexibility by offering a wide range of instance sizes, operating systems, and pre-configured templates. This flexibility enables you to deploy and modify server environments rapidly, reducing time to market for your applications.
- Cost-efficiency: Cloud servers follow a pay-as-you-go model, allowing you to pay only for the resources you consume. This eliminates the need for upfront investments and provides cost-efficiency, particularly for small to medium-sized businesses or projects with variable resource needs.
Downsides of Cloud Servers:
- Performance Variability: Since cloud servers are virtualized, they may experience performance variations due to shared resources. High traffic from other users on the same physical infrastructure could impact performance, leading to inconsistent response times.
- Dependency on the Provider: Relying on a cloud service provider means you are subject to their service level agreements (SLAs) and potential downtime or service disruptions. Any issues on the provider’s end can impact your applications’ availability and performance.
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Cloud servers may raise concerns regarding data privacy and compliance, particularly if your application handles sensitive data. Ensuring compliance with specific regulations may require additional measures, such as data encryption or geographical restrictions.
Examples and When to Choose Bare Metal or Cloud Servers
Use Cases for Bare Metal Servers:
- High-performance applications: If your application requires consistent and maximum performance without resource sharing, such as data-intensive analytics or gaming servers, bare metal servers are a preferred choice.
- Compliance and data privacy: Bare metal servers are suitable for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as healthcare or finance, where data privacy and compliance are paramount.
- Resource-intensive workloads: Applications that heavily rely on CPU, memory, or disk I/O, such as video rendering or scientific simulations, can benefit from dedicated hardware resources provided by bare metal servers.
Use Cases for Cloud Servers:
- Scalable web applications: Cloud servers are ideal for web applications with variable traffic patterns, allowing you to scale resources up or down based on demand. This is beneficial for e-commerce sites, media streaming platforms, or applications experiencing unpredictable user spikes.
- Development and testing environments: Cloud servers provide flexibility and rapid provisioning, making them valuable for developers who need on-demand environments for testing, staging, or continuous integration processes.
- Startups and small businesses: Cloud servers offer cost-efficiency for businesses with limited budgets and resources. They eliminate the need for large upfront investments and provide the flexibility to scale as the business grows.
It’s important to note that hybrid approaches can also be considered, where you combine the benefits of both bare metal and cloud servers. For example, you might utilize bare metal servers for the core database and backend processes while using cloud servers for front-end web servers or load balancing.
Ultimately, the choice between bare metal and cloud servers depends on your specific needs, priorities, and the characteristics of your applications. Consider factors such as performance requirements, scalability, customization, data privacy, compliance, and budget to make an informed decision that aligns with your objectives.